Green board gets specified all the time. Half the time, it’s wrong.
Some people treat it like waterproofing. Others skip it entirely and hope paint does the job. The truth sits somewhere in between, and that gap is where most drywall problems start.
Green board has a purpose, limits, and a few common misuse patterns that lead to repeat repairs. We’ll break down what green board is, where it works, where it fails, and how to choose the right board before anything goes back in the wall.
Key Notes
Green board performs like standard drywall in dry rooms, but lasts longer in humid, ventilated spaces.
Appropriate for bathrooms outside wet zones, kitchens, basements, and post-leak repairs.
Costs ~15–25% more, with value tied to reduced sagging, mold risk, and repeat repairs.
What Is Green Board Drywall?
Green board drywall is a moisture‑resistant type of drywall designed for spaces that deal with humidity, steam, or the occasional splash, but not constant water.
If you’ve ever opened up a bathroom wall or kitchen backsplash and noticed drywall with a green paper face, that’s green board.
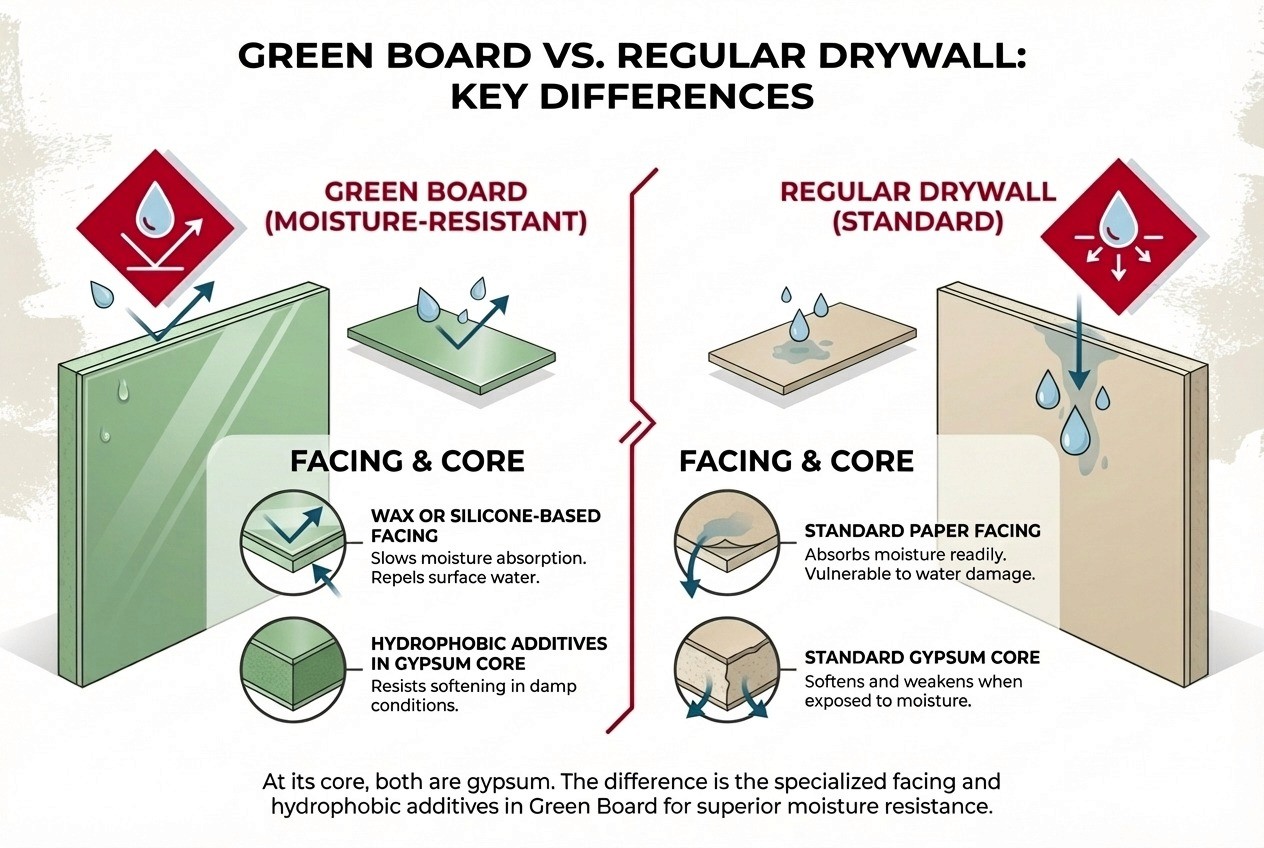
Green board is moisture-resistant, not waterproof. It’s meant to tolerate humidity better than standard drywall, not survive direct water exposure or repeated soaking.
Used correctly, it reduces long‑term damage and mold risk.
Used incorrectly, it fails just like regular drywall.
How Green Board Is Made (& Why It Resists Moisture)
Green board’s performance comes from two components working together:
The Green Paper Facing
The visible green paper isn’t cosmetic. It’s treated with water‑repellent compounds that cause moisture to bead rather than soak in immediately. This slows down surface absorption from steam, splashes, or humid air.
It’s the first line of defense, not a seal.
The Gypsum Core
Inside the board, the gypsum is infused with hydrophobic additives such as waxes or silicones. These additives make the core denser and less prone to breaking down when moisture gets past the paper.
The Combined Effect
Together, the facing and core:
Slow moisture absorption
Reduce softening and sagging in humid rooms
Delay mold growth compared to standard drywall
What they don’t do is block water indefinitely. Prolonged exposure still leads to deterioration.
Green Board vs Regular Drywall
Green board and standard drywall look similar once installed and painted. The difference shows up over time, especially in damp environments.
Feature | Green Board | Standard Drywall |
Moisture resistance | Moderate | Low |
Mold resistance | Better than standard | Poor in humid areas |
Cost | ~15–25% higher | Lowest |
Dry room performance | Same | Same |
Wet area suitability | Limited | Not suitable |
In dry, conditioned spaces, they perform identically. In humid rooms, standard drywall absorbs moisture faster, swells, softens, and becomes a mold risk much sooner.
What Is Green Board Used For?
Green board is a selective material, not an upgrade for an entire house. It’s best suited for rooms where humidity is elevated but water exposure is intermittent.
Common uses include:
Bathrooms (outside shower and tub enclosures)
Kitchens, especially behind sinks and backsplashes
Laundry rooms
Basements
Garages
Areas previously affected by leaks or water damage
The goal isn’t waterproofing. The goal is durability in spaces where moisture is part of normal use.

Green Board in Bathrooms
Bathrooms are the most common place green board shows up, and also where it’s most misunderstood.
Green board works well on:
Vanity walls
Toilet areas
Upper wall sections exposed to steam
Bathroom ceilings with proper ventilation
👉 It does not belong in direct wet zones.
Even with good exhaust fans, bathrooms experience repeated humidity spikes. Green board tolerates that environment better than standard drywall and holds paint, texture, and tile finishes longer.
Green Board After Water Damage
Installing green board after water damage only works if the underlying problem is resolved first.
Before any new drywall goes up:
The moisture source must be identified and fixed
All affected materials must be removed
Framing and cavities must be fully dried
Best Practices Include:
Removing drywall and insulation at least 12–24 inches above the damage line
Drying studs to below 15–16% moisture content
Treating any mold on framing
Restoring insulation and vapor barriers correctly
Green board helps prevent repeat issues. It does not mask unresolved ones.
Mold Resistance: What Green Board Prevents
Green board reduces mold risk. It does not eliminate it.
The treated paper slows moisture uptake, which delays mold growth in intermittently humid conditions. But the paper facing is still organic. Given enough moisture and time, mold can still grow.
Mold prevention depends more on:
Ventilation
Drying
Leak control
Correct material selection
Green board buys time. It doesn’t override poor conditions.
Cost of Green Board Drywall
Green board drywall typically costs about 15–25% more than standard drywall.
That difference usually translates to:
A small material upcharge
Minimal impact on labor costs
In most projects, the real value is longevity. Avoiding early failure and mold repairs often outweighs the initial cost difference.
When Green Board Is the Right Choice (& When It’s Not)
Green board is the right choice when:
Humidity is elevated but controlled
Direct water contact is limited
Ventilation is adequate
You want added protection without overbuilding
It’s the wrong choice when:
Water exposure is constant
Waterproofing is required
The moisture source isn’t resolved
Frequently Asked Questions
Can green board be painted like regular drywall?
Yes. Green board can be primed, painted, or textured the same way as standard drywall. The key is using a quality primer so moisture doesn’t migrate through paint layers in humid rooms.
Does green board require special installation or fasteners?
No special fasteners are required, but spacing and fastening need to be tight in humid areas. Poor fastening can lead to sagging over time, especially on ceilings.
Can green board be used on ceilings?
Yes, but only in areas with good ventilation. In steamy bathrooms, ceiling use requires proper framing support and exhaust fans to prevent long-term moisture buildup.
How long does green board last compared to regular drywall?
In humid spaces, green board lasts significantly longer because it resists moisture absorption. In dry rooms, both materials perform the same over their lifespan.
Not Sure Which Drywall Applies?
We’ll recommend the right fix for your space.
Conclusion
Green board isn’t a magic fix. That’s the part most people miss.
What green board really comes down to is understanding limits. It’s drywall built to handle humidity, steam, and the occasional splash better than standard board. It works well in bathrooms outside the shower, kitchens, basements, and repair areas after leaks. It fails when it’s treated like waterproofing.
Used in the wrong spot, it softens, sags, and feeds mold just like any other drywall. Used correctly, it helps walls last longer and keeps repairs from repeating.
If you want a clear answer on what material makes sense for your space, moisture levels, and repair scope, getting eyes on the details is what matters. Get a quick quote to confirm the right materials and get proper installation backed by a one-year workmanship guarantee.





